Solutions, Solubility, and Colligative Properties Chemistry Visionlearning
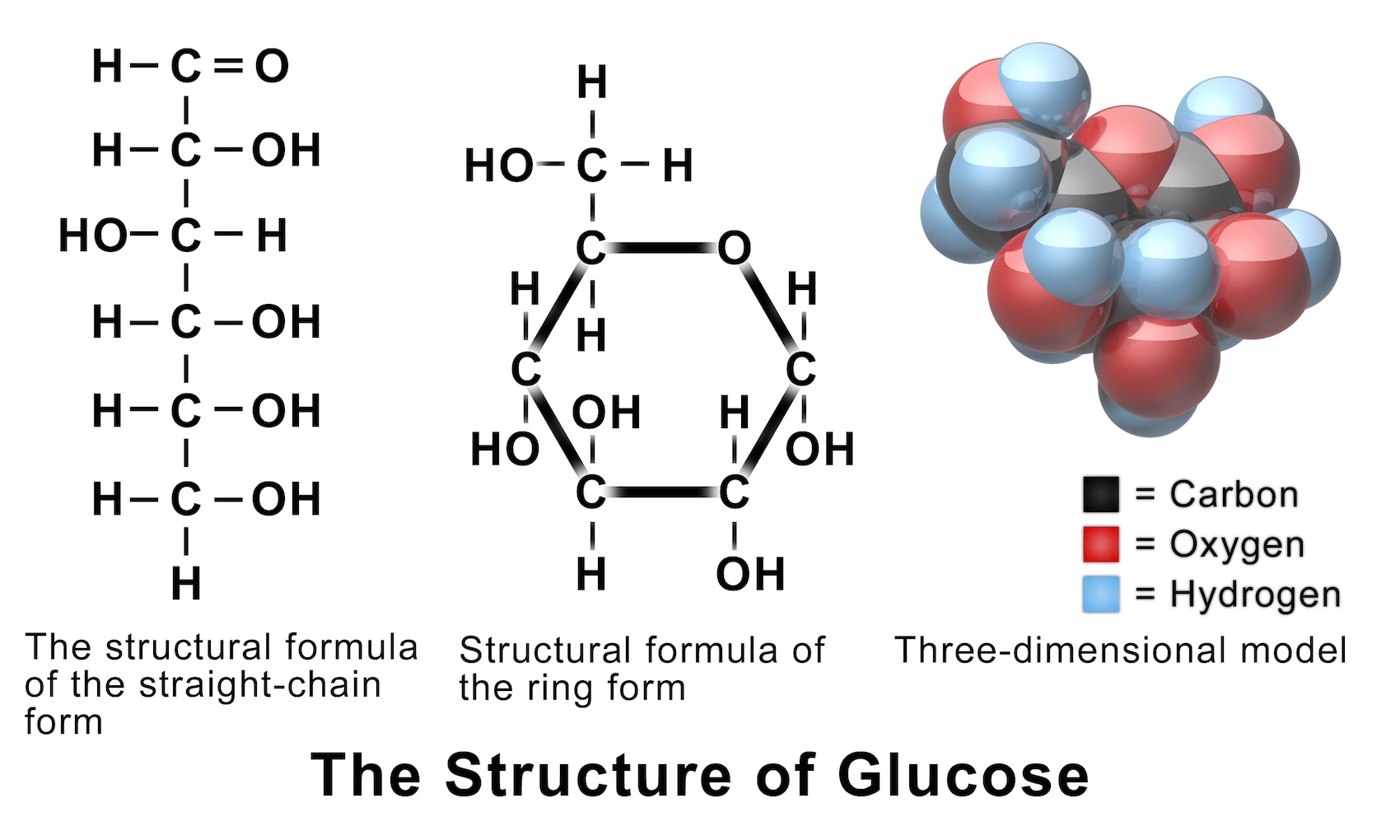
Summary. Glucose is the most important monosaccharide that provides energy to cells present in our bodies. It is an aldohexose having an aldehydic group and multiple hydroxyl groups attached to six carbon atoms. Its structure can be represented by an open-chain structure or a closed ring. Glucose has 16 isomers.
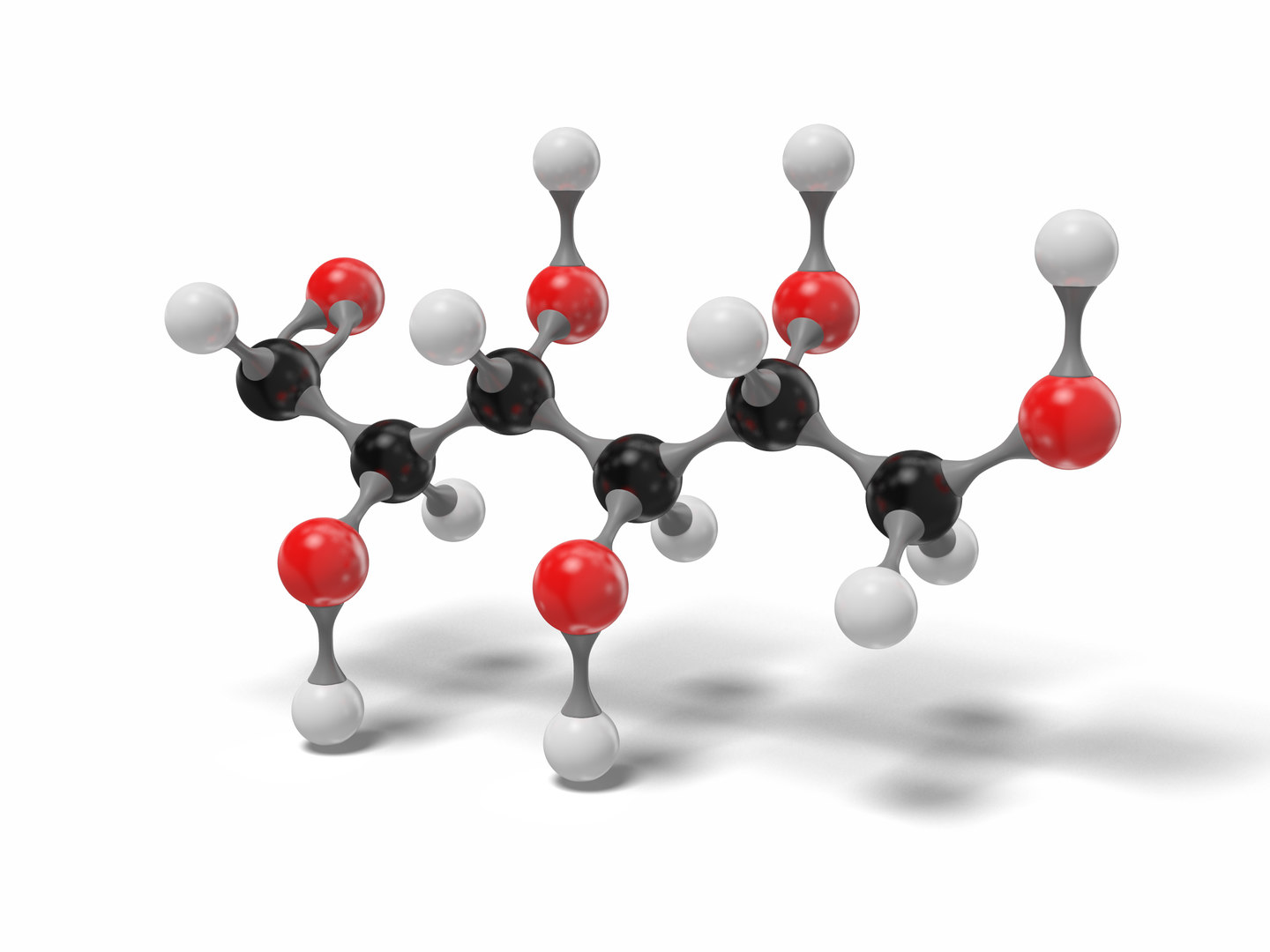
3D glucose open chain molecule model TurboSquid 1570289
Google Classroom Overview of carbohydrates, including structure and properties of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Introduction What's in a spud? Besides water, which makes up most of the potato's weight, there's a little fat, a little protein…and a whole lot of carbohydrate (about 37 grams in a medium potato).
4 simple steps to drawing chain structure of glucose molecule
In sucrose, a glycosidic linkage is formed between carbon 1 in glucose and carbon 2 in fructose. Common disaccharides include lactose, maltose, and sucrose (Figure 3.2.5 3.2. 5 ). Lactose is a disaccharide consisting of the monomers glucose and galactose. It is found naturally in milk.

Structural chemical formula and model glucose Vector Image
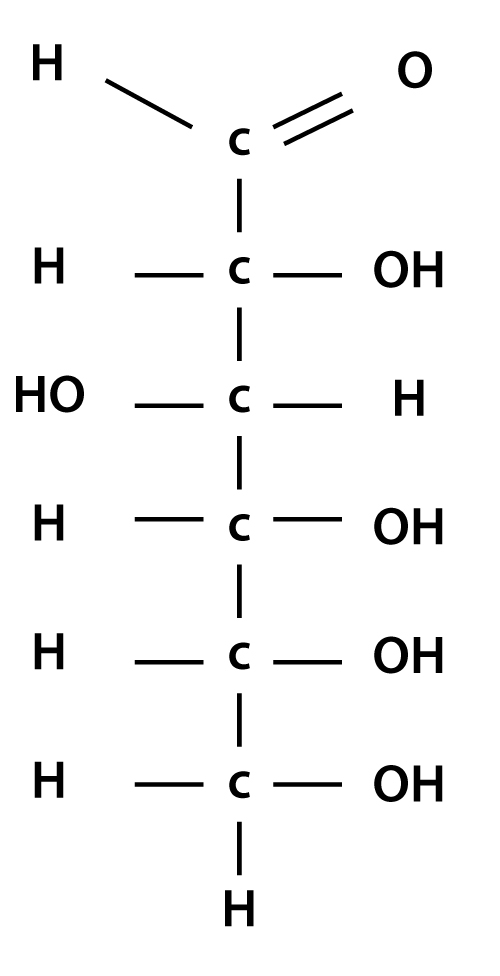
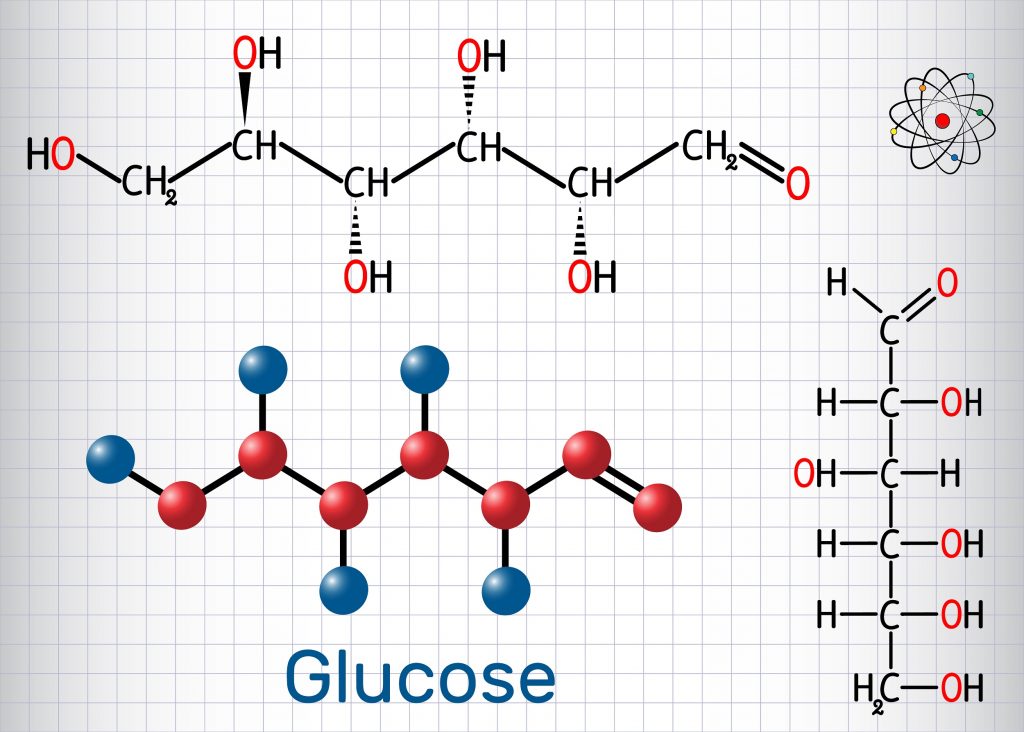
Steps to Draw Open Chain Structure of a Glucose Molecule Follow the steps given below to draw an acyclic form of glucose. Step 1: Draw 6 carbon atoms Step 2: Draw extended arms for all the carbon atoms excluding the first one. Step 3: Now draw hydrogen to carbon bond such that four are on one side and one on the other side.

Basics of Carbohydrates
Glucose Structure Open-Chain Formula The open-chain formula of glucose can be constructed with the following facts: Molecular formula: From the analysis of elements of glucose and from the molecular weight of glucose, the molecular formula, that is, C 6 H 12 O 6, is established.
Glucose Chain Structure
Molecular structure of glucose (video) | Khan Academy Biology library Course: Biology library > Unit 5 Lesson 2: Carbohydrates Molecular structure of glucose Dehydration synthesis or a condensation reaction Hydrolysis Molecular structure of fructose Carbohydrates Carbohydrates Science > Biology library > Macromolecules > Carbohydrates
3D model glucose molecule modeled TurboSquid 1542502
Glucose (from Greek glykys; "sweet") has the molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major free sugar circulating in the blood of higher animals. It is the source of energy in cell function, and the regulation of its metabolism is of great importance ( see fermentation; gluconeogenesis ).
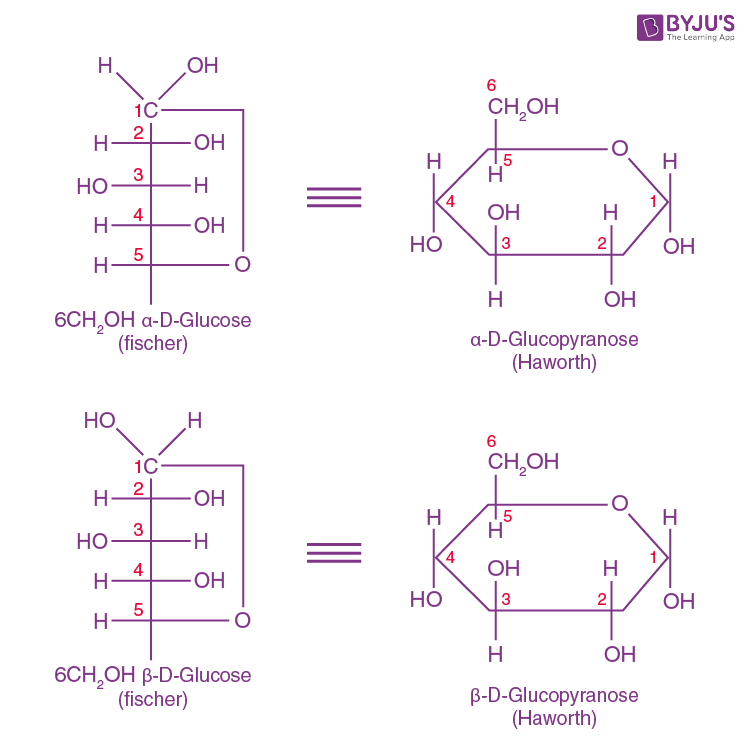
Glucose Structure Diagrams, Examples, Physical Properties
Figure 8.2.1:Glucose and fructose are monosaccharides, or simple sugars. Glucose and fructose are both soluble in water. In aqueous solution, the predominant forms are not the straight-chain structure shown above. Rather, they adopt a cyclic structure (see figure below). Glucose is six membered ring, while fructose is a five-membered ring.

Glucose structure and function Zogor
Structure of glucose Carbohydrates are composed of naturally occurring organic compounds of carbon-hydrogen and oxygen, which are primarily produced by plants. Carbohydrates are formed by plants by a process known as photosynthesis. The general formula of carbohydrates is Cm (H2O)n

Glucose Structure, Properties, Synthesis, Facts & Summary
Open-Chain Formula of Glucose Structure The open-chain formula of glucose can be determined by considering the following facts: Molecular formula: The molecular formula, C 6 H 12 O 6, is established from the analysis of glucose's elements and its molecular weight.
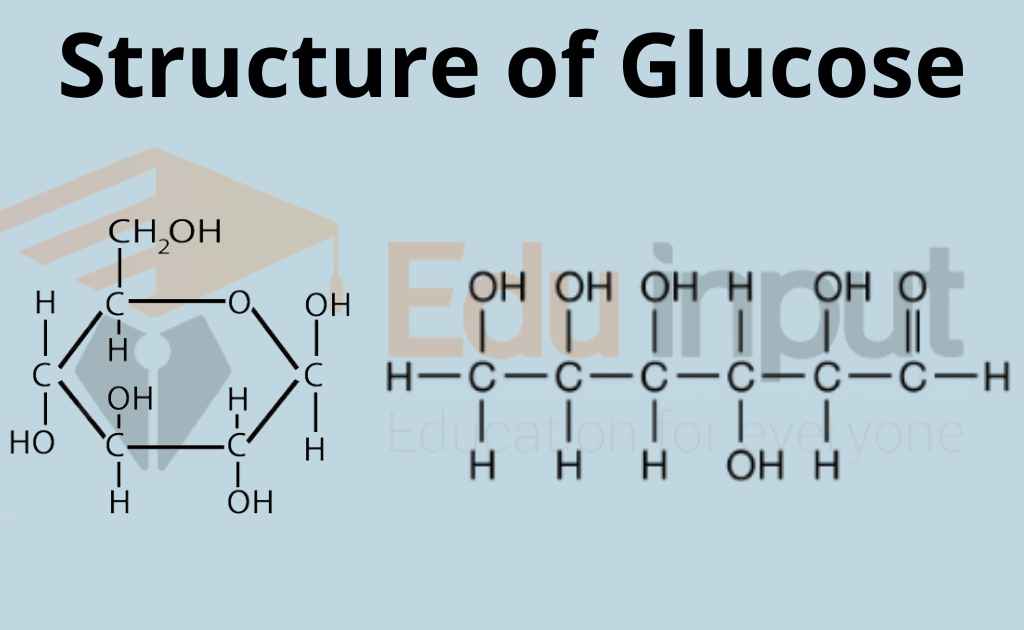
What is Glucose?Glucose in Plants, Animals, and Humans
Glucose is a 6-carbon structure with the chemical formula C6H12O6. It is a ubiquitous source of energy for every organism in the world and is essential to fuel both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. Glucose often enters the body in isometric forms such as galactose and fructose (monosaccharides), lactose and sucrose (disaccharides), or starch (polysaccharide).

What is Biomolecules Definition of Biomolecules, Notes, Examples, Books
Chemical and physical properties Glucose forms white or colorless solids that are highly soluble in water and acetic acid but poorly soluble in methanol and ethanol.
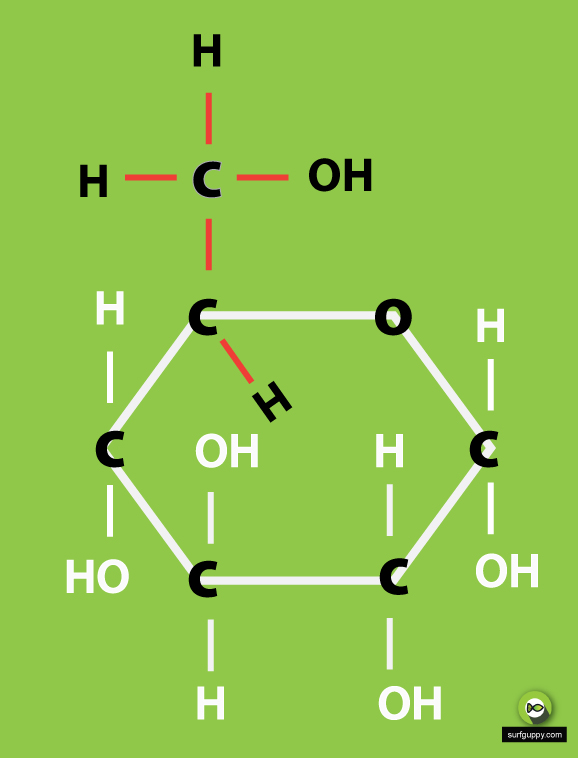
3 Simple Steps Draw the ring structure of glucose molecule
Glucose is central to energy consumption. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins all ultimately break down into glucose, which then serves as the primary metabolic fuel of mammals and the universal fuel of the fetus. It serves as the major precursor for the synthesis of different carbohydrates like glycogen, ribose, and deoxyribose, galactose, glycolipids, glycoproteins, and proteoglycans.

Glucose 3D Model C6H12O6 3D model CGTrader
21: Carbohydrates 21.4: Structure of Glucose and Other Monosaccharides
Is glucose healthy?
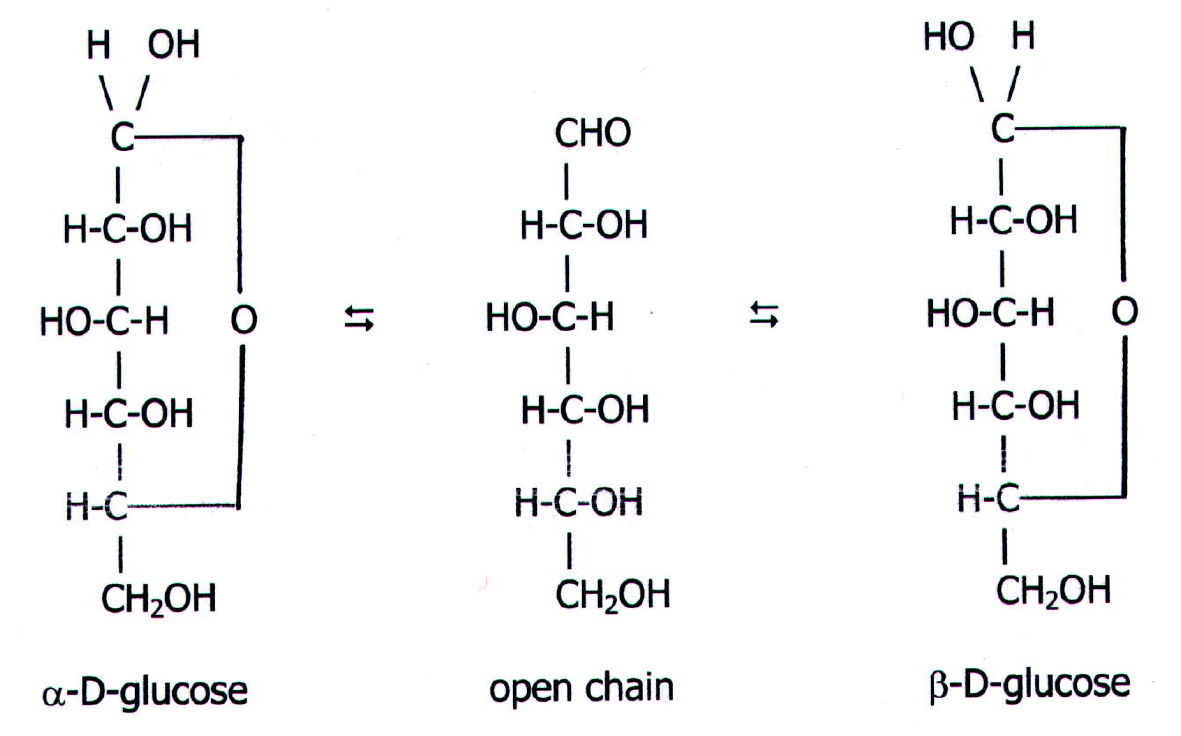
At equilibrium, the mixture consists of about 36% α-D-glucose, 64% β-D-glucose, and less than 0.02% of the open-chain aldehyde form. The observed rotation of this solution is +52.7°. Even though only a small percentage of the molecules are in the open-chain aldehyde form at any time, the solution will nevertheless exhibit the characteristic reactions of an aldehyde.

Classification of Carbohydrates with Types, Formula and Structure
Learn to draw the open chain structure and ring structure in easy to follow steps. Note that there are in fact 3 versions of the ring structure. I have shown.