
(PDF) DirectContact Heat Transfer
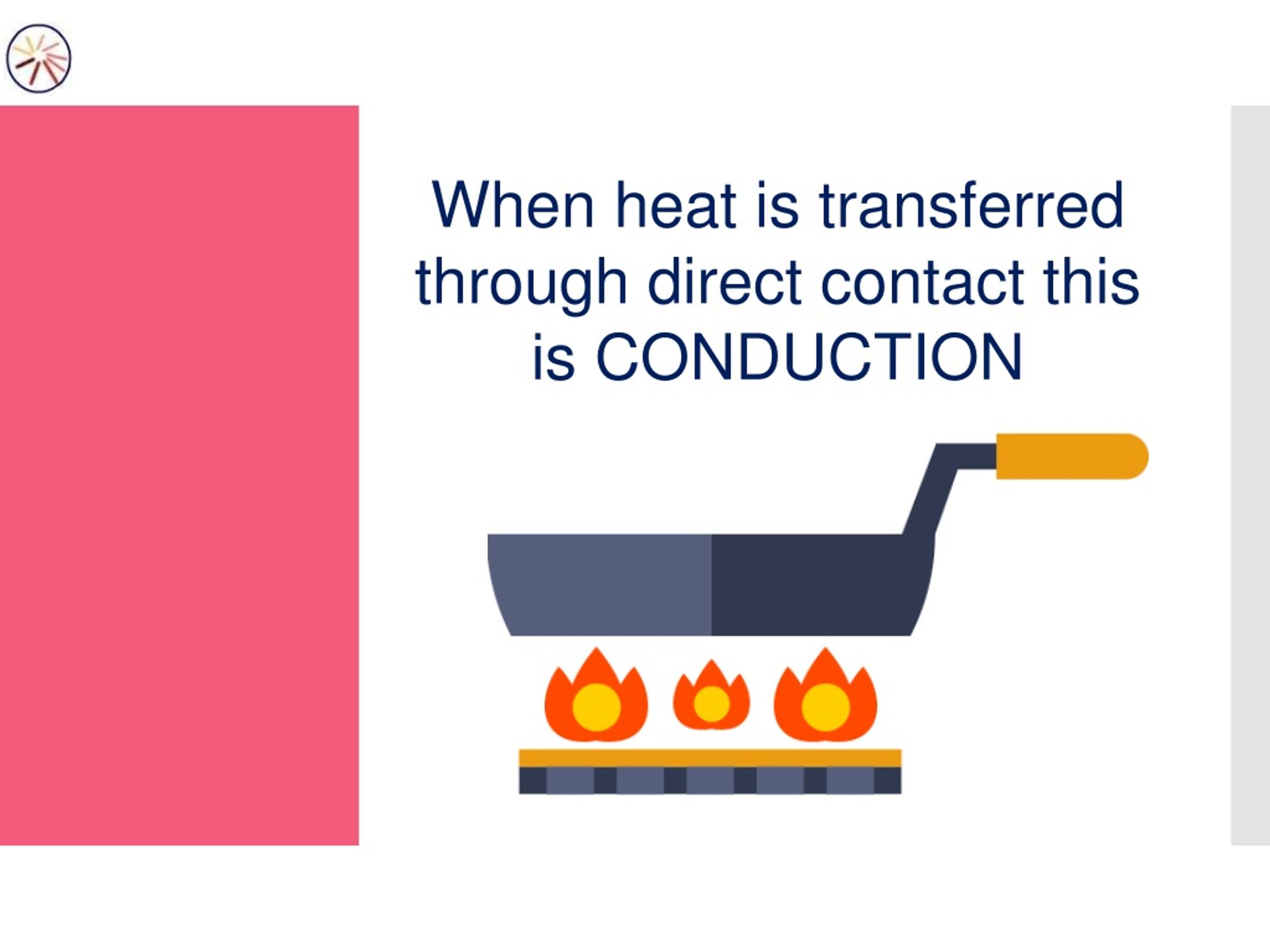
Heat conduction is the transfer of heat between two objects in direct contact with each other. The rate of heat transfer Q/t (energy per unit time) is proportional to the temperature difference T2 −T1 and the contact area A and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects: Q t = kA(T2 −T1) d. (8.6.12)

Direct Thermal Vs. Thermal Transfer What's the Difference? YouTube
Q = mcΔT, Q = m c Δ T, 11.7. where m is the mass of the substance and Δ T is the change in its temperature, in units of Celsius or Kelvin. The symbol c stands for specific heat, and depends on the material and phase. The specific heat is the amount of heat necessary to change the temperature of 1.00 kg of mass by 1.00 ºC.

HeatTransfer Basics Impressions
477061. A heat exchanger is a device used to transfer heat between two or more fluids. The fluids can be single or two phase and, depending on the exchanger type, may be separated or in direct contact. Devices involving energy sources such as nuclear fuel pins or fired heaters are not normally regarded as heat exchangers although many of the.

Methods of heat transfer stock vector. Illustration of kitchen 193604538
Heat is the transfer of energy between objects at different temperatures. This is a really important concept, so let's write that definition out. Heat is the transfer of energy between objects at different temperatures. As you can see with our pizza and plate, heat is transferring from the hot pizza to the cold plate, from the hot object to the.

A Guide on How To Heat A Warehouse Powrmatic
Heat is used to raise the temperature of air so that Q = mcΔT Q = m c Δ T. The rate of heat transfer is then Q t Q t, where t t is the time for air turnover. We are given that ΔT Δ T is 10.0ºC, but we must still find values for the mass of air and its specific heat before we can calculate QQ.

Transfer processing of heat energy HEAT WORLD OF PHYSICS
The direct heat transfer systems also results in high dust and emissions. All emissions must be cleaned before being released back into the atmosphere in order to comply with pollution and environmental controls. INDIRECT HEATING TECHNOLOGY. In the last 25 years, a more efficient and cost effective method has been introduced, using indirect.

Large Format Direct To Fabric Heat Transfer Paper Sublimation Printer
In classical heat exchangers, heat transfer takes place through a wall separating the hot and the cold fluid streams. Thus, conventional heat exchangers are limited in their ability to tap the maximum thermodynamic potential because they have built-in thermal losses associated with the separation of the fluid streams by an intervening solid wall.

Heat Transfer Definition, Mechanisms & Application
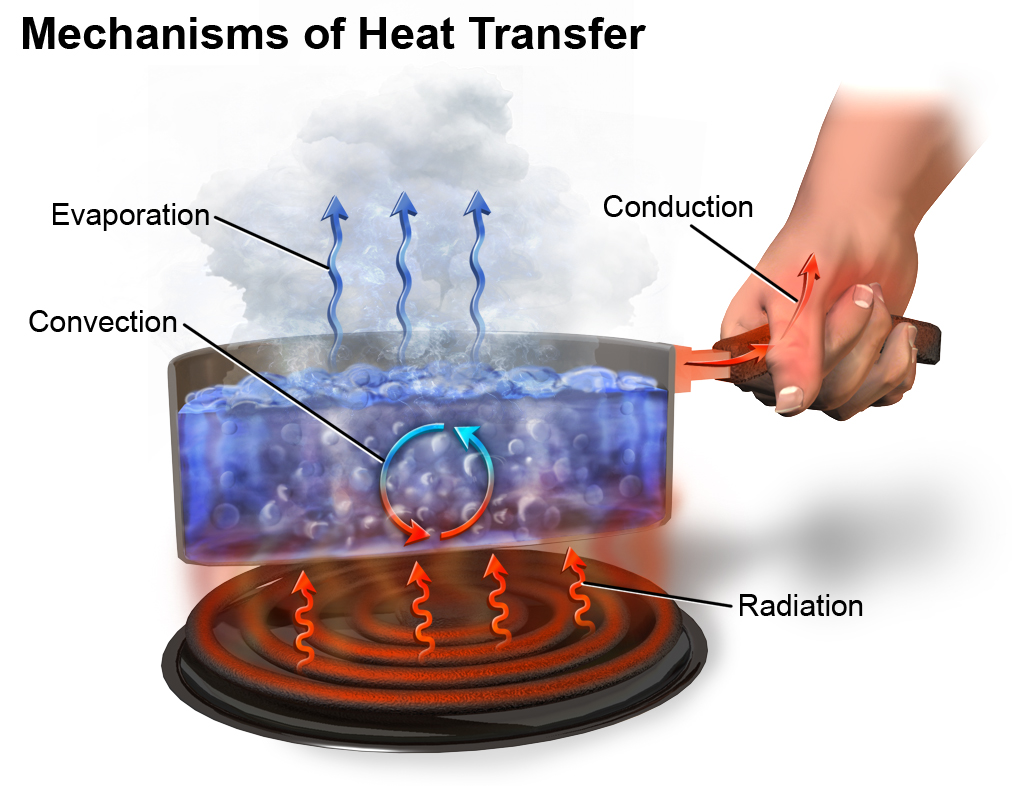
The three types of heat transfer differ according to the nature of the medium that transmits heat: Conduction requires contact. Convection requires fluid flow. Radiation does not require any medium. Conduction is heat transfer directly between neighboring atoms or molecules. Usually, it is heat transfer through a solid.

Examples of Heat Transfer Through Conduction in daily life
Direct-contact heat transfer involves the exchange of heat between two immiscible fluids by bringing them into contact at different temperatures. There are two basic bubbling regimes in direct-contact heat exchanger: homogeneous and heterogeneous. Industrially, however, the homogeneous bubbling regime is less likely to prevail, owing to the high gas flow rates employed. The mixture homogeneity.
การถ่ายโอนความร้อน (Heat Transfer) Tuemaster เรียนออนไลน์ ม.ปลาย
AboutTranscript. There are three forms of thermal energy transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves molecules transferring kinetic energy to one another through collisions. Convection occurs when hot air rises, allowing cooler air to come in and be heated. Thermal radiation happens when accelerated charged particles.

3 Methods of Heat Transfer YouTube
heat transfer coefficient. Direct contact boiling phenomena have been proposed for a variety of applications, including nuclear reactors. A proposal has been presented (Kinoshita and Nishi, 1994.

4 Common Heat Transfer Vinyl Issues and How to Fix Them FiredOut
A typical direct contactor provides heat transfer between two fluid streams. The processes include the simple heating or cooling of one fluid by the other; cooling with the vaporization of the coolant; cooling of a gas-vapor mixture with partial condensation; cooling of a vapor or vapor mixture with total condensation; and cooling of a liquid with partial or complete solidification.

How long does heat transfer paper last on a shirt The News God
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy between physical systems.. Condensation on direct contact with a cooling wall of a heat exchanger: This is the most common mode used in industry:

Opinions on Heat transfer
The distribution of heat production in each layer can be considered as the sum of components with different wavelengths λ, denoted A (λ). The amount of heat generated by each component is H λ = Δ A λ. For a layer at depth z, the component of the surface heat flow Q (λ) is given by. (6) Q λ = H λ 2 π λ Δ × exp − 2 π z λ × 1 −.
PPT Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
51223. Direct contact heat transfer is generally defined as heat transfer between two or more mass streams without the presence of an intervening wall. The mass streams can be cocurrent, countercurrent or even crossflow. The streams can be immiscible or miscible or partly so. Typical two-stream direct contactors include: liquid-liquid, liquid.
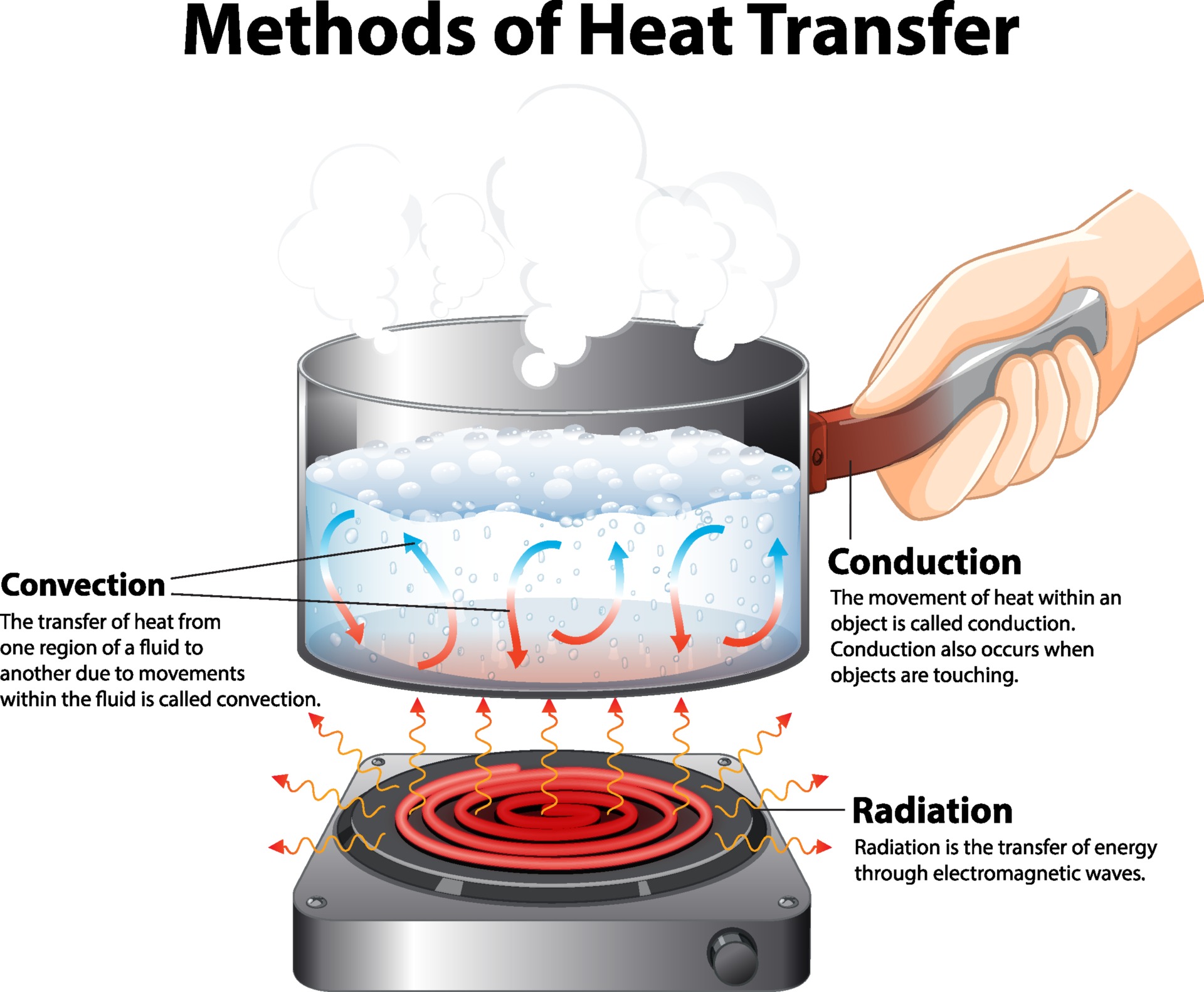
Diagram showing Methods of Heat Transfer 2790593 Vector Art at Vecteezy
There are two thermal printing methods: direct thermal and thermal transfer. Each method uses a thermal printhead that applies heat to the surface being marked. Direct thermal printing uses chemically treated, heat-sensitive media that blackens when it passes under the thermal printhead, while thermal transfer printing uses a heated ribbon to.