Thermal transmittance (Uvalue) tecscience

What is the Uvalue? Simply explained insights by LAMILUX
U-values (sometimes referred to as heat transfer coefficients or thermal transmittances) are a measure of how effective the elements of a building's fabric are as insulators. That is, the degree to which they prevent heat from transmitting between the inside and the outside of a building.
PPT Heat Loss and Gain PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Heat loss through common building elements due to transmission, R-values and U-values - imperial and SI units. The heat transmission through a building wall or similar construction can be expressed as: The overall heat transfer coefficient - the U-value - describes how well a building element conducts heat or the rate of transfer of heat (in.

Thermal transmittance (Uvalue) tecscience
R-value and U-factor are the inverse of one another: U = 1/R. Materials that are very good at resisting the flow of heat (high R-value, low U-factor) can serve as insulation materials. So far, so good. Materials have another property that can affect their energy performance in certain situations: heat capacity. Heat capacity is a measure of how.

A Quick and Easy Guide to UValues
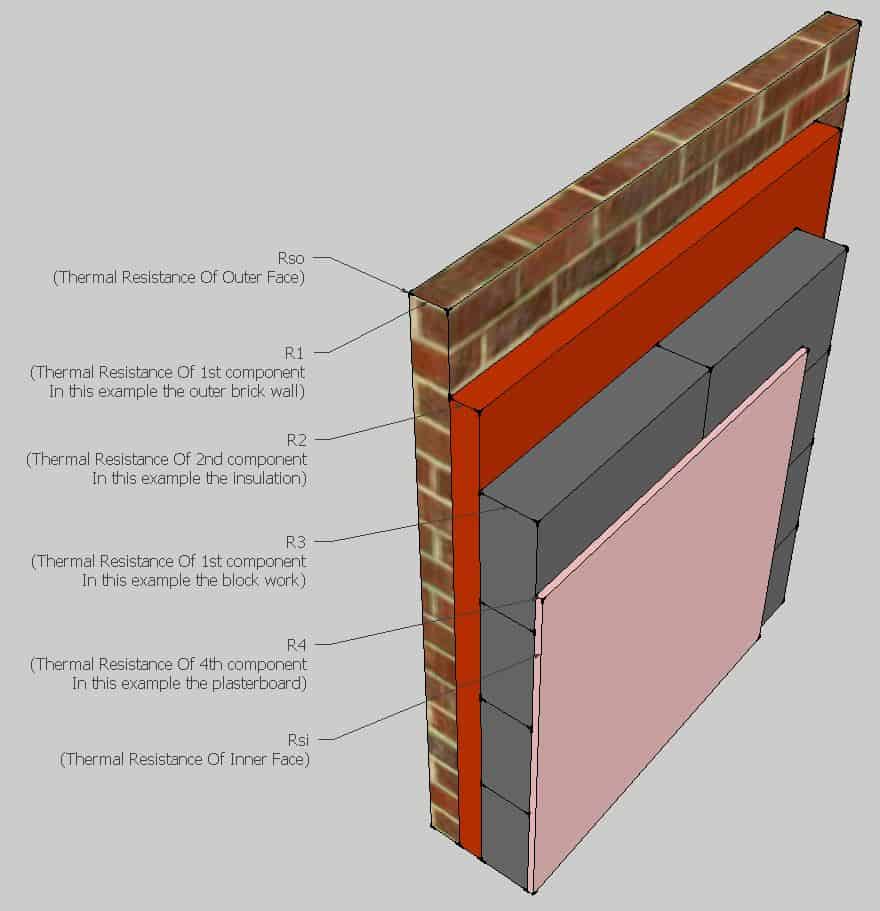
A U-value is the total of the thermal resistances (explained below) of the layers that make up an entire building element - for example, a Roof (slates, felt, joists, insulation), Wall (blocks, insulation, plaster) or Floor (concrete, sand, DPM, insulation & flooring). It also includes adjustments for any fixings or air gaps, this is critical.

PPT Temperature and Heat Loss PowerPoint Presentation, free download
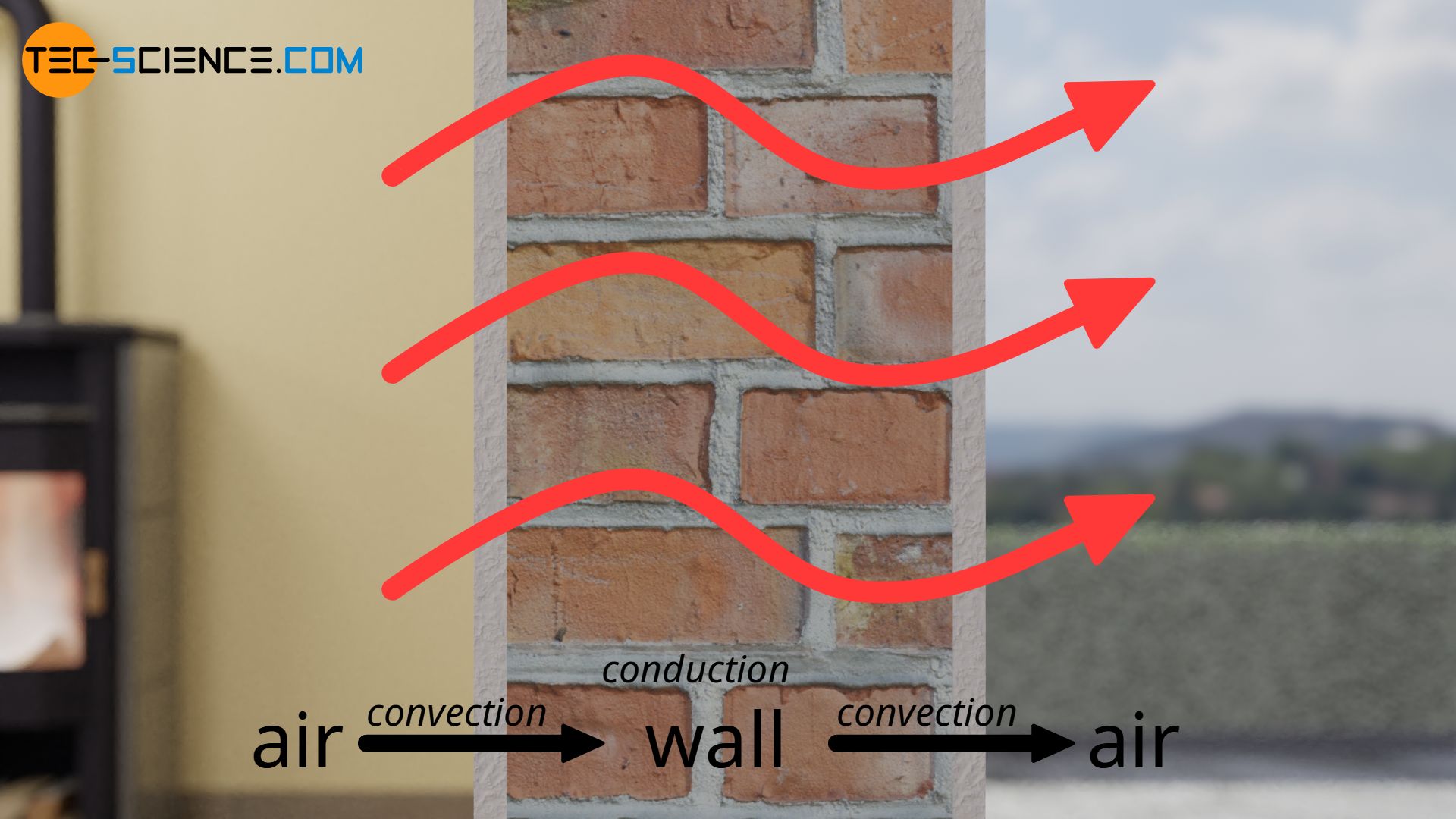
However, this applies only within 'reasonable' limits, usually quite well especially in the building sector for many constructions with various materials. The 'largely constant' proportionality factor is called the thermal transmittance or U-value of the component. This is a measure of the heat transmittance of a component for each unit of area.
Thermal transmittance (Uvalue) tecscience
Approximate Heat loss = U-value (W/m2K) x Temperature difference (inside and outside) x Surface area (m2) For example, let's say: So, the approximate heat loss = 0.25 x 25 x 100 = 625 W to keep the temperature inside at 22 degrees. You will need to calculate the approximate heat loss for roof, walls, floors, doors, and windows to find the.
How To Calculate U Values In Buildings & Free Calculator Tool
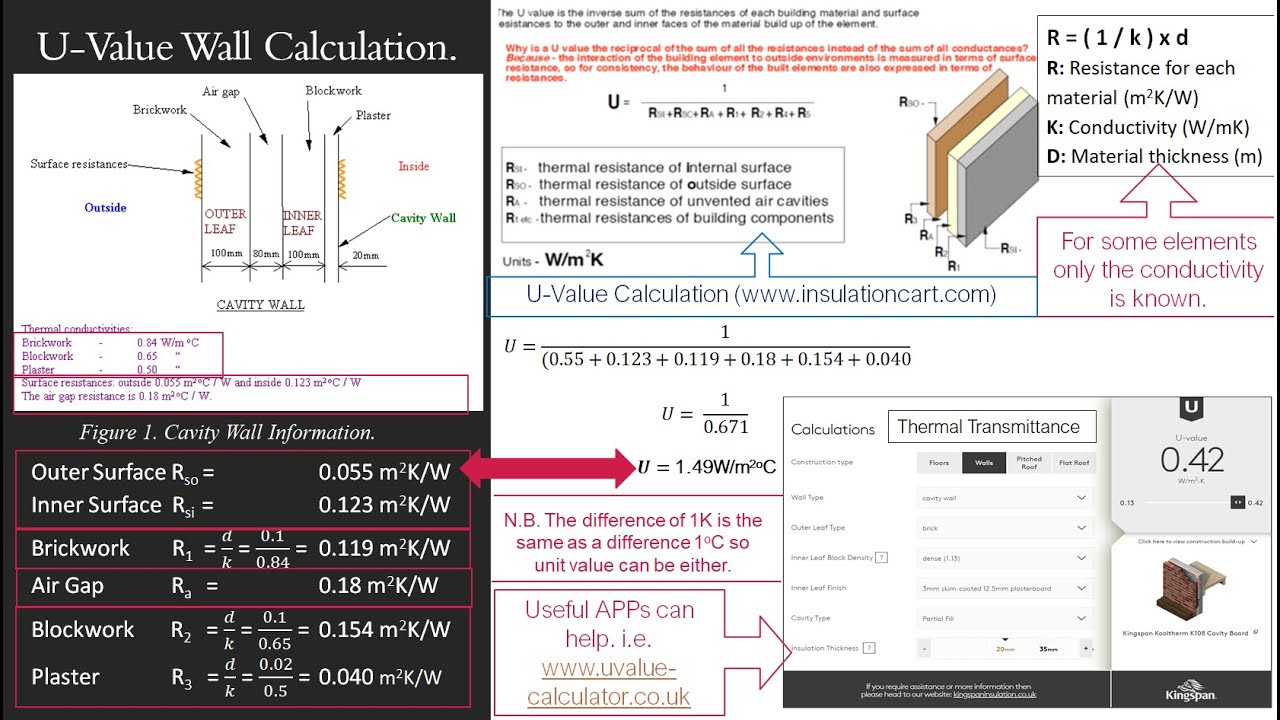
U-values are calculated using the thermal conductivity (lambda or K value) of each material in the construction; their thickness and also the thermal resistance of the external and internal surfaces of the construction. The lower the lambda value of a material, the better an insulator it is.
Thermal Calculations UValue of Wall YouTube
Thermal transmittance, also known as U-value, is the rate of transfer of heat through a structure (which can be a single material or a composite), divided by the difference in temperature across that structure. The better the insulation is on a structure the lower the U-value will be. If the insulation is fitted poorly, with gaps and cold.
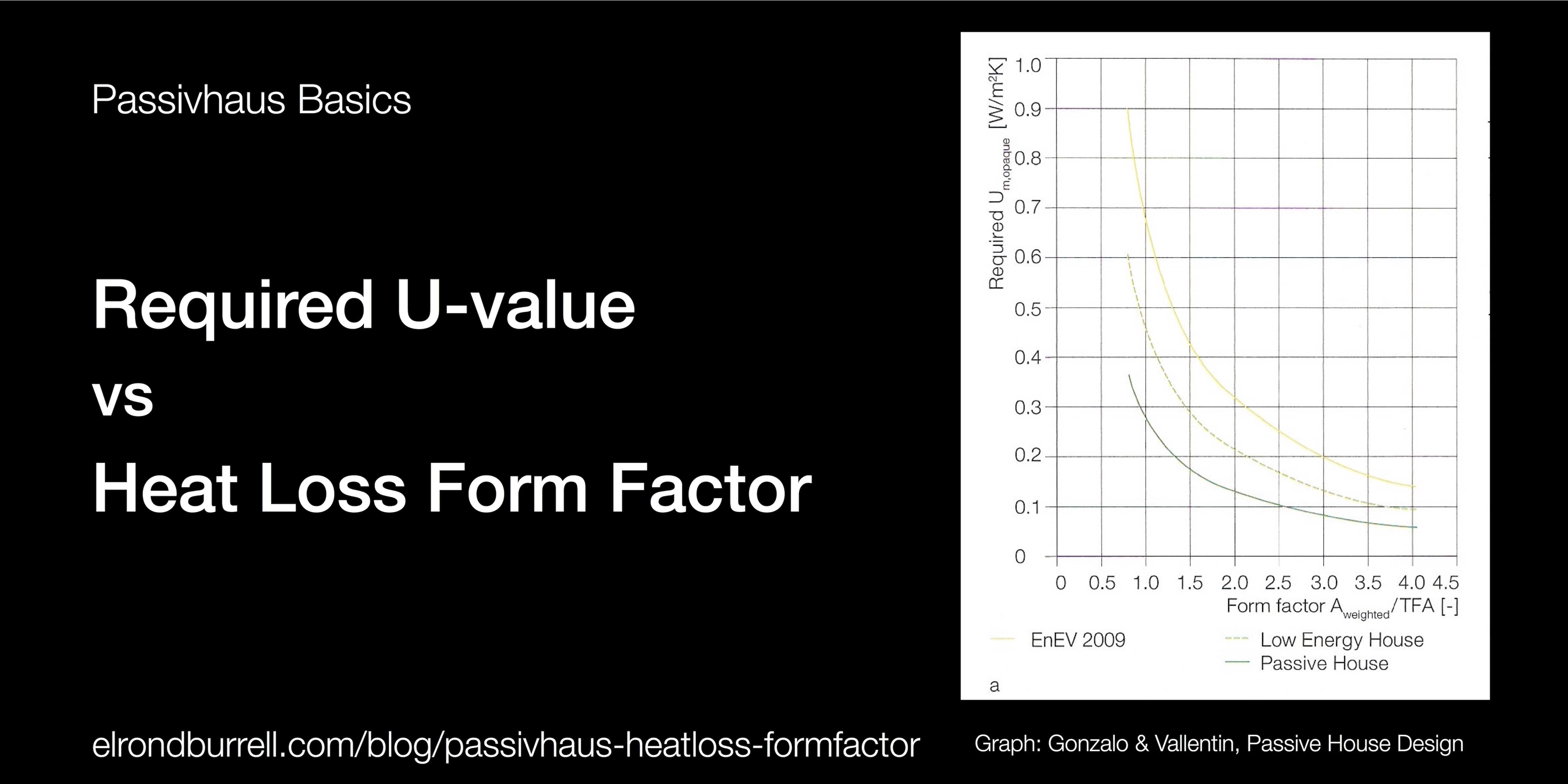
What is the Heat Loss Form Factor? PASSIVHAUS IN PLAIN ENGLISH & MORE
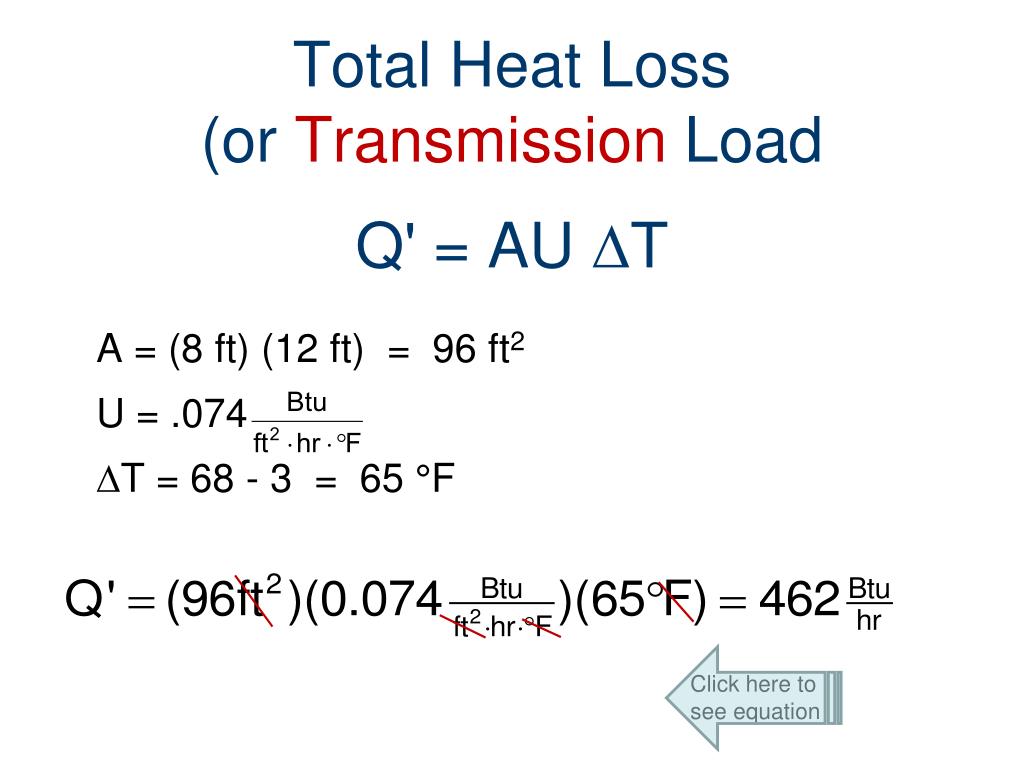
Calculating the Building Heat Loss Rate using "U" values: (Building Heat Loss in BTU's per hour) U = 1/R, - or in other words -. (Building Total Surface Area in sq.ft.) x (Surface Area "U" value) x (Temperature Difference) Thanks to Steven Muscato for correcting this formula.

What is a Uvalue? Heat loss, thermal mass and online calculators
Unless the property is made from elastic, the surface area can't change and the U-Values are absolutely fixed too, since they're a property of the specific building materials. From this, we can simply say that fabric heat loss is a result of: Surface Area x U-Value x (inside temp - outside temp). Heat Loss = A x U x ∆T. Or. Q = AU∆T
Thermal Mass Calculator Calculator Academy
The U-value of insulation is a value that is used to measure how well a specific type of insulation can resist heat flow.The lower the U-value, the more effective the material is at preventing heat transfer. The U-value is very closely linked to the R-value, as it simply represents its inverse.The U-value is also closely connected to the idea of thermal conductivity, which is a property of a.
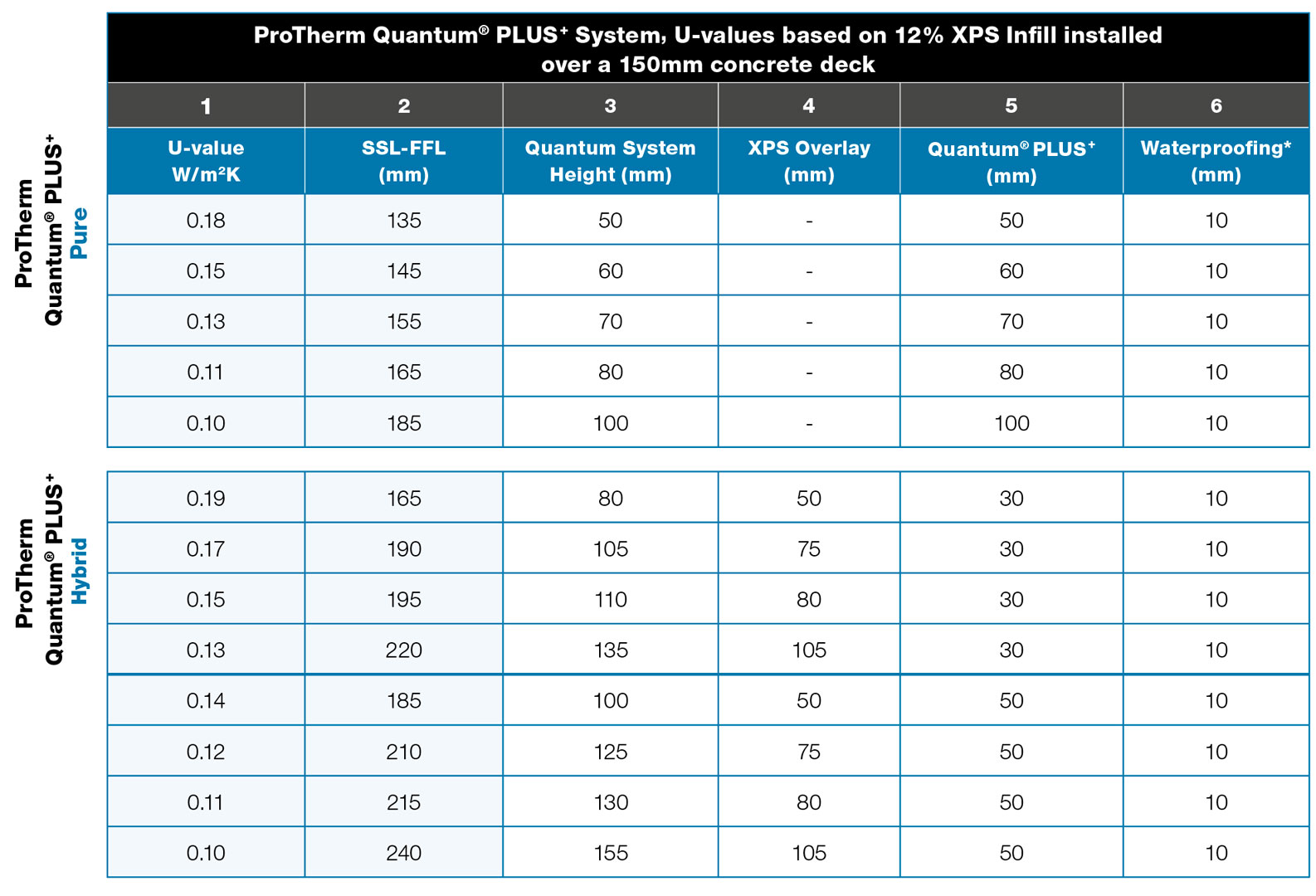
Quantum PLUS+ Uvalues Radmat
The U-value U indicates how much heat energy per unit time and unit area is transmitted through a solid object at a temperature difference of the fluids of 1 Kelvin (1 °C). The U-Value is therefore also called thermal transmittance .The U-value is therefore given in the unit "Watt per square meter and Kelvin" W/ (m²⋅K).
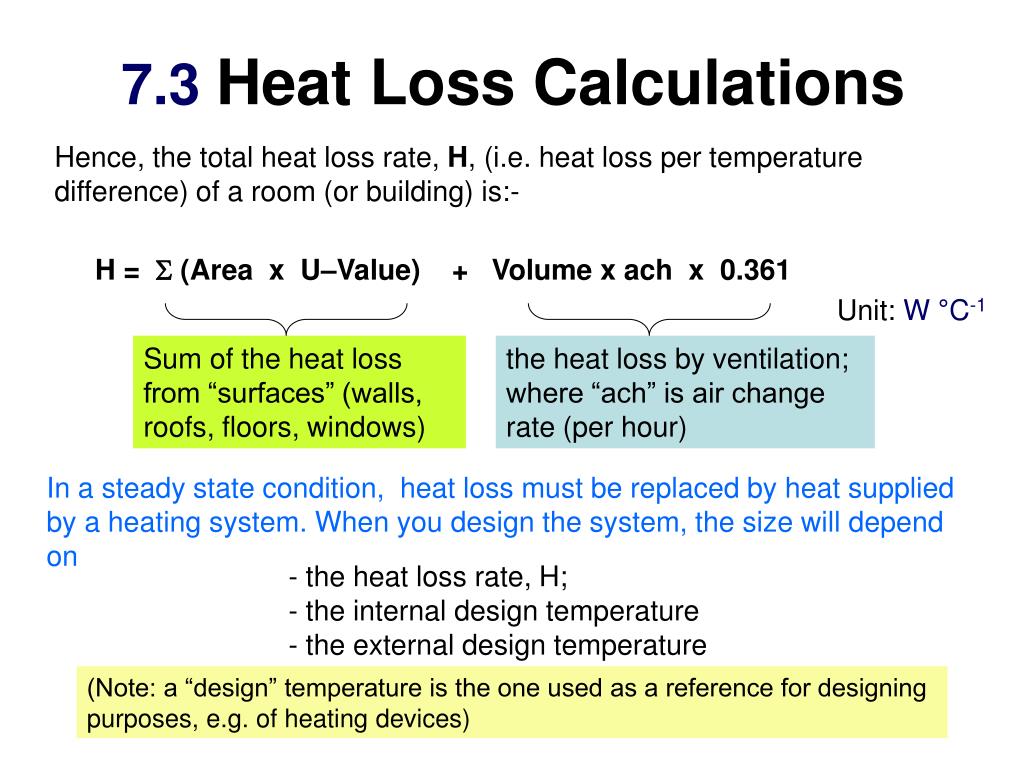
PPT Section 7 HEAT LOSS CALCULATIONS PowerPoint Presentation, free
Heat_loss = Area × U-value, where: Area is the area of the surface, U-value is the U-value of the material. The heat loss through walls can be estimated in the following way. First, we should specify the type of insulation. In our calculator, we have provided 3 options: no extra insulation: solid brick wall, 9" thick, U-value = 2.2 W/(m²·K)
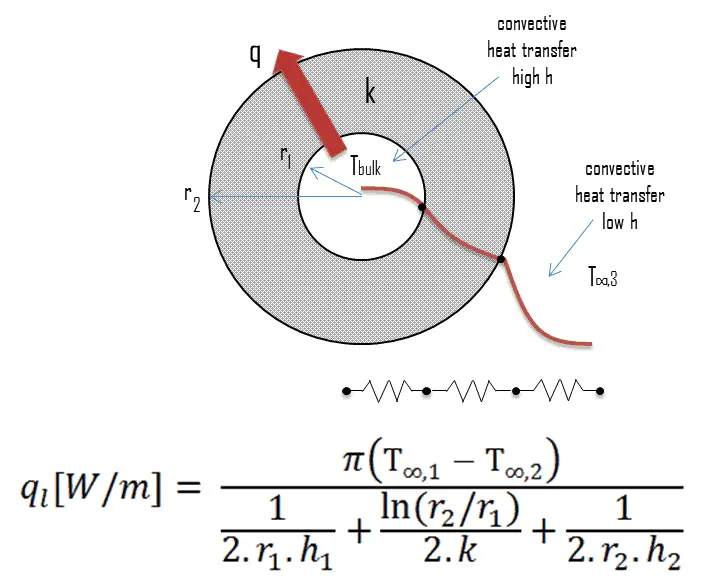
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Ufactor Definition nuclear
Thermal transmittance, also known as U-value, is the rate of transfer of heat through a structure (which can be a single material or a composite), divided by the difference in temperature across that structure. The units of measurement are W/m²K. The better-insulated a structure is, the lower the U-value will be.

U value or Thermal Transmittance I How to calculate U Value YouTube
The ROCKWOOL U-value calculator is a free, online tool designed to help specifiers, selfbuilders and construction stakeholders to calculate U-values for their individual projects using ROCKWOOL stone wool insulation. With up-to-date information on ROCKWOOL solutions and a series of BIM objects, users can quickly and easily calculate accurate U.

Temperature and Heat Loss Thermal conductivity Thermal conductivity
Formula of U-Value Calculator. The formula for calculating the U-Value (W/m²K) involves the summation of thermal resistances (Ri) multiplied by their respective thicknesses (Di), divided by the sum of the thicknesses of all layers. See also Indirect Water Heater Sizing Calculator Online. U-value (W/m²K) = Σ (Ri * Di) / ΣDi.